A tumor is an abnormal growth of cells that can occur anywhere in the body. While not all tumors are cancerous, they require attention as they can disrupt normal bodily functions or develop into more severe conditions. This comprehensive blog will explore the types of tumors, their symptoms and causes, risk factors, complications, diagnostic methods, and treatment options, with a special focus on stem cell therapy and the potential role of SALUD Extra in tumor management.
What is a Tumor?
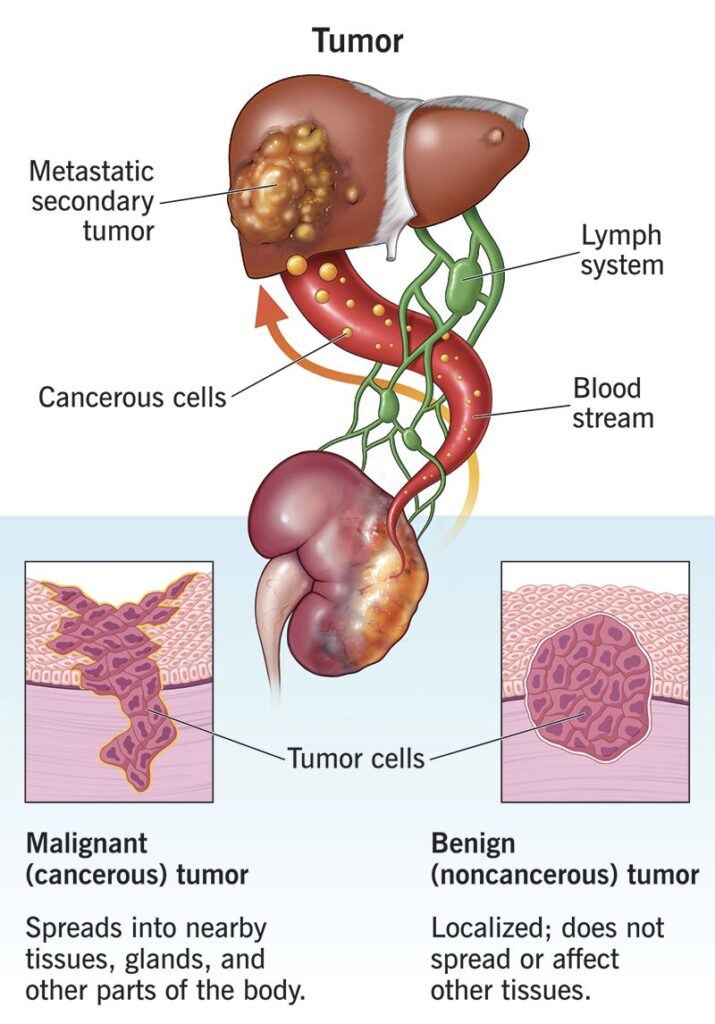
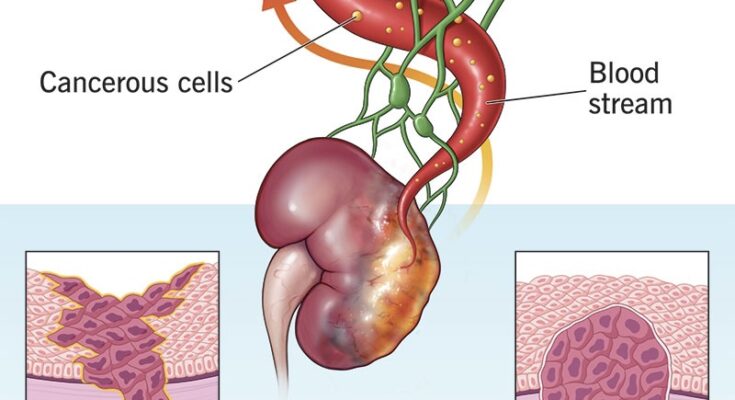
A tumor, also called a neoplasm, is the result of cells growing uncontrollably and forming a mass or lump. Tumors can be categorized as:
- Benign (Non-cancerous): These tumors grow slowly and do not spread to other parts of the body.
- Malignant (Cancerous): These are aggressive and can invade nearby tissues or metastasize (spread) to other parts of the body.
- Precancerous: Abnormal cells that have the potential to become cancerous but are not yet malignant.
Types of Tumors
Benign Tumors:
- Lipomas: Fat tissue growths, often found under the skin.
- Fibroids: Non-cancerous growths in the uterus.
- Hemangiomas: Growth of blood vessels, common in infants.
Malignant Tumors (Cancers):
- Carcinomas: Originate in epithelial cells (e.g., breast, lung, prostate cancers).
- Sarcomas: Begin in connective tissues like bone or muscle.
- Leukemias: Blood cancers that start in bone marrow.
- Lymphomas: Cancer of the lymphatic system.
Other Tumor Types:
- Brain Tumors: Can be benign or malignant, affecting neurological function.
- Germ Cell Tumors: Originate in reproductive cells, such as in the ovaries or testes.
Symptoms and Causes of Tumors
Symptoms:
Symptoms depend on the tumor’s size, location, and whether it is benign or malignant:
- General Symptoms:
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
- Pain or discomfort in the affected area
- Lumps or masses (visible or felt under the skin)
- Neurological symptoms (headaches, seizures) for brain tumors
- Changes in bowel or bladder habits for abdominal tumors
Causes:
- Genetic mutations leading to uncontrolled cell growth.
- Exposure to carcinogens (e.g., tobacco smoke, radiation, chemicals).
- Family history of tumors or cancer.
- Viral infections, such as HPV or Hepatitis B/C, which can trigger tumor development.
Risk Factors
Several factors increase the risk of developing a tumor:
- Age: Risk increases with age due to cumulative cell damage.
- Lifestyle Choices: Smoking, alcohol consumption, and poor diet.
- Environmental Factors: Prolonged exposure to harmful chemicals or radiation.
- Chronic Conditions: Diabetes, obesity, or certain infections like HIV.
Complications of Tumors
Tumors, especially malignant ones, can lead to:
- Compression of nearby organs, causing pain and dysfunction.
- Blockages in essential systems, like blood vessels or airways.
- Metastasis, spreading cancer to vital organs.
- Side effects of treatment, such as immunosuppression or organ damage.
Diagnosis and Tests
Initial Assessment:
- Physical examination to check for lumps or abnormal growths.
- Patient history, including symptoms and risk factors.
Diagnostic Tests:
Imaging Tests:
- X-rays: For bone tumors or detecting masses.
- MRI/CT Scans: Detailed images of internal organs and tissues.
Biopsy:
- Tissue sample analysis to determine if the tumor is benign or malignant.
Blood Tests:
- Identify tumor markers like PSA (Prostate-Specific Antigen) or CA-125.
Management and Treatment
Traditional Treatments:
- Surgery: Removing the tumor entirely if accessible.
- Radiation Therapy: Targeted radiation to destroy cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Systemic drug therapy to kill rapidly growing cells.
Emerging Therapies:
- Immunotherapy: Boosts the immune system to fight cancer.
- Targeted Therapy: Drugs targeting specific genetic mutations in tumor cells.
Stem Cell Therapy for Treating Tumors
Stem cell therapy is a promising approach in cancer treatment, focusing on regenerative medicine and immune response enhancement.
How Stem Cell Therapy Works:
- Regeneration: Stem cells can repair damaged tissues caused by cancer or its treatment.
- Targeted Delivery: Stem cells can be engineered to deliver anti-tumor agents directly to cancerous cells.
- Immunomodulation: Helps strengthen the immune system to combat cancer cells.
Advantages of Stem Cell Therapy:
- Minimally invasive.
- Reduced side effects compared to traditional treatments.
- Potential for personalized medicine.
SALUD Extra: A Breakthrough in Stem Cell Therapy

SALUD Extra is an advanced supplement designed to harness the power of stem cell therapy in tumor management. It supports the body’s natural regenerative processes, making it an effective option for tumor treatment and overall health improvement.
Benefits of SALUD Extra:
- Stimulates Stem Cell Production: Promotes the generation of new, healthy cells to repair and regenerate tissues.
- Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Reduces inflammation, which can worsen tumor progression.
- Boosts Immunity: Enhances the body’s natural defense against abnormal cell growth.
- Detoxification: Helps cleanse the body of toxins that contribute to cell mutations.
How SALUD Extra Can Help with Tumors:
- Supports recovery after surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy.
- Helps manage symptoms like fatigue, inflammation, and weakened immunity.
- Complements traditional and modern cancer treatments.
Conclusion
Tumors, whether benign or malignant, require careful attention and management to prevent complications and ensure the best possible outcomes. Understanding the types, symptoms, causes, and available treatment options is essential for early detection and effective intervention. While traditional treatments like surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation remain vital, innovative approaches such as stem cell therapy offer hope for more targeted and less invasive care.
SALUD Extra stands out as a promising supplement in tumor management, leveraging the regenerative power of stem cells to repair damaged tissues, reduce inflammation, and strengthen the immune system. By integrating products like SALUD Extra with comprehensive medical care, individuals facing tumor-related challenges can experience improved quality of life and better recovery prospects.
Early diagnosis, informed decisions, and the adoption of cutting-edge therapies are key to combating tumors effectively. Stay proactive about your health, consult medical professionals regularly, and explore advanced solutions like SALUD Extra for a healthier, more hopeful future.