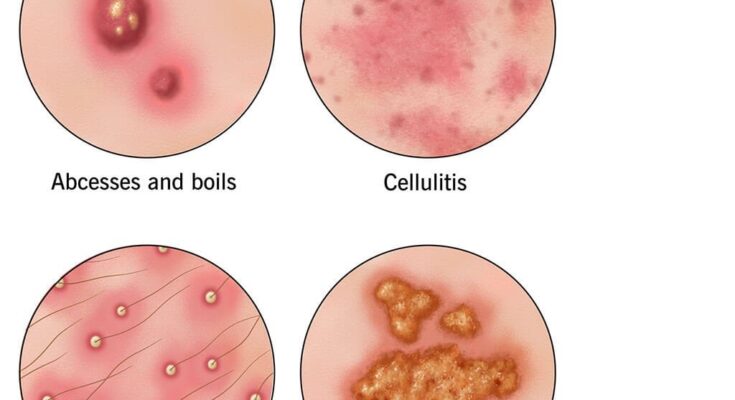
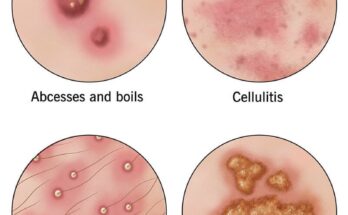
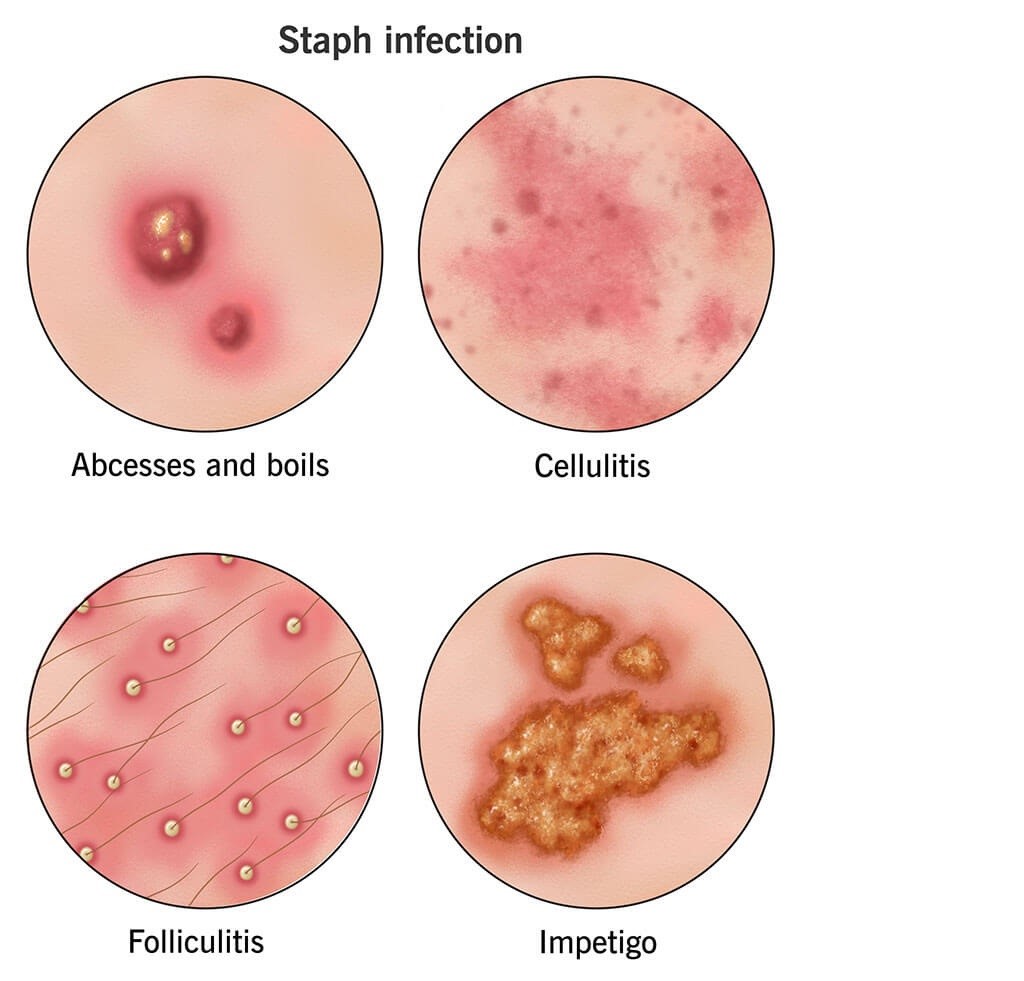
A staph infection is caused by Staphylococcus bacteria, a group of bacteria that can be found on the skin and in the noses of many people without causing harm. However, when these bacteria enter the body through cuts, abrasions, or other openings, they can cause a range of infections, some of which can be serious or even life-threatening.
Overview
What is a Staph Infection?
A staph infection is an infection caused by the bacteria Staphylococcus. These bacteria are typically found on the skin or in the nasal passages of healthy individuals. However, when the skin is broken—such as through a cut, scrape, or other wound—the bacteria can enter the body and cause an infection. Some strains of staph bacteria, such as Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), are resistant to certain antibiotics, making them harder to treat.
What Parts of Your Body Are Affected by Staph Infection?
Staph infections can affect various parts of the body, ranging from superficial skin infections to more serious conditions. Common areas impacted include:
- Skin: Staph often causes pimples, boils, impetigo (a contagious skin infection), and cellulitis (a deep skin infection).
- Bones and joints: In severe cases, staph can infect bones (osteomyelitis) and joints (septic arthritis).
- Bloodstream: If staph enters the bloodstream, it can lead to sepsis, a life-threatening condition.
- Lungs: Staph can cause pneumonia, which can be particularly dangerous for those with weakened immune systems.
- Heart: In rare cases, staph can infect the heart valves (endocarditis), leading to severe complications.
How Common is Staph Infection?
Staph infections are quite common, with Staphylococcus aureus being one of the most prevalent bacteria found on human skin. It’s estimated that up to 30% of people carry Staphylococcus aureus in their nasal passages without any signs of infection. However, the actual number of people who develop active staph infections is lower. While anyone can develop a staph infection, certain individuals may be at higher risk.
Who Does Staph Infection Affect?
Staph infections can affect anyone, but some groups are at higher risk:
- Children: Staph infections are common in children, particularly in the form of skin conditions like impetigo or boils.
- People with weakened immune systems: Those undergoing chemotherapy, organ transplant recipients, or individuals with conditions like diabetes or HIV are more susceptible.
- Athletes: People who participate in contact sports are at a higher risk due to the possibility of cuts and abrasions that can become infected.
- Healthcare workers: Due to frequent exposure to patients with infections, healthcare workers are also at increased risk.
What Kinds of Staph Infections Do Children Get?
Children are particularly vulnerable to staph infections, especially skin infections. Some common types of staph infections in children include:
- Impetigo: A highly contagious skin infection causing red sores that can ooze and form a yellow-brown crust.
- Boils: These are painful, pus-filled bumps that develop under the skin.
- Cellulitis: A bacterial infection affecting the deeper layers of skin, causing redness, swelling, and warmth.
Symptoms and Causes
What Are the Signs and Symptoms of a Staph Infection on the Skin?
On the skin, staph infections can present as:
- Red, swollen, painful areas of the skin
- Pus-filled boils or abscesses
- Blisters or scabs
- Fever (in more severe cases)
- Warmth around the infected area
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s important to seek medical attention, especially if they worsen.
What Are the Signs and Symptoms of a Staph Infection in the Body?
In more severe staph infections, the symptoms can extend beyond the skin and affect other parts of the body:
- Fever and chills
- Low blood pressure
- Fatigue or malaise
- Rapid breathing or difficulty breathing (if lungs are infected)
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Joint pain and swelling (if joints are infected)
How Do People Get a Staph Infection?
Staph infections spread through direct contact with an infected wound, nasal discharge, or contaminated surfaces. People can also contract staph infections from sharing personal items, such as towels, razors, or sports equipment. Staph bacteria thrive in warm, moist environments, so individuals who sweat a lot (athletes, gym-goers) are particularly at risk.
Diagnosis and Tests
How Is Staph Infection Diagnosed?
A healthcare provider typically diagnoses a staph infection through:
- Physical examination: The provider will inspect the infected area for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, and discharge.
- Laboratory tests: A sample of the pus or wound drainage may be collected and tested in a laboratory to identify the specific strain of Staphylococcus.
How Do I Know if I Have a Staph Infection?
You may have a staph infection if you notice symptoms such as skin redness, swelling, pain, or the appearance of boils or abscesses. If the infection spreads or affects other parts of your body, such as your lungs or bloodstream, you may experience fever, chills, and body aches. If you suspect a staph infection, it’s important to consult a doctor promptly to avoid complications.
Management and Treatment
What Are the Treatments for Staph Infection?
The treatment for staph infections depends on the type and severity of the infection. Common treatments include:
- Antibiotics: Oral or topical antibiotics are used to treat most staph skin infections. If the infection is more severe or caused by MRSA, intravenous antibiotics may be necessary.
- Drainage of abscesses: If an abscess or boil forms, it may need to be drained by a healthcare provider.
In more severe cases, like bloodstream infections, surgical intervention might be required to remove infected tissue.
Stem Cell Therapy for Staph Infection
Recent studies have explored the potential of stem cell therapy as a novel treatment for staph infections, especially in cases where conventional antibiotics fail due to antibiotic resistance. Stem cells may help by boosting the body’s immune response and promoting tissue repair. Stem cell-based treatments like Faforon and Spidex19 have shown promise in early trials for treating infections, though they are still under investigation and not yet widely used.
Stem Cell Treatment

While traditional antibiotics are often effective for treating these infections, the rise of antibiotic resistance has led to the exploration of alternative treatments, including stem cell therapies. Faforon and Spidex 19 are two stem cell-based treatments that have garnered attention for their potential benefits in managing staph infections. Although still under investigation, these therapies show promising results in both reducing the severity of infections and promoting quicker recovery.
Here’s a closer look at the potential benefits of Faforon and Spidex 19 in the treatment of staph infections:
- Boosting the Immune System
Both Faforon and Spidex 19 have been found to enhance the body’s natural immune response. Stem cells can help regenerate damaged tissues, support the immune system, and promote healing. In the case of a staph infection, these therapies may help the body fight off the bacterial infection more effectively. Stem cells can stimulate the production of cytokines and other immune cells that are crucial for combating bacterial invaders, potentially reducing the severity and duration of the infection
- Reducing Inflammation and Tissue Damage
Staph infections, particularly severe ones like MRSA, can lead to extensive tissue damage and inflammation. Stem cells in Faforon and Spidex 19 have been shown to possess anti-inflammatory properties, which may help reduce swelling, pain, and redness associated with staph infections. By minimizing the inflammatory response, these therapies could prevent complications such as scarring or long-term tissue damage, particularly in skin and joint infections.
- Promoting Faster Healing and Regeneration
One of the most promising benefits of Faforon and Spidex 19 is their ability to promote tissue regeneration and healing. Stem cells have the unique capability to differentiate into various types of cells, which allows them to repair and regenerate damaged tissues. In the case of staph infections, where skin and deeper tissues are often compromised, stem cell therapy could accelerate the healing process. This is particularly beneficial for patients with chronic or recurrent infections that are slow to heal or have developed resistance to conventional treatments.
- Reducing the Risk of Antibiotic Resistance
Antibiotic resistance is one of the biggest challenges in treating staph infections, especially with the rise of MRSA. Faforon and Spidex 19 do not rely on antibiotics to treat infections, which means they offer an alternative approach to managing these resistant strains. While antibiotics can lose their effectiveness over time due to resistance, stem cell therapies work by directly enhancing the body’s immune system and healing processes, offering a potential solution to infections that may not respond well to traditional treatments.
- Targeting Biofilms
Staph bacteria, particularly MRSA, are known to form biofilms—a protective layer that shields the bacteria from the immune system and antibiotics. This makes staph infections difficult to treat and often leads to chronic or recurrent infections. Some studies suggest that stem cells may help disrupt biofilms, allowing the immune system to target and eliminate the bacteria more effectively. By helping to break down these protective barriers, Faforon and Spidex 19 may offer a novel way to combat stubborn staph infections.
- Lowering the Risk of Complications
Severe staph infections can lead to complications such as sepsis, pneumonia, and endocarditis. These complications can be life-threatening, especially in patients with weakened immune systems. Stem cell therapies like Faforon and Spidex 19 have the potential to reduce the risk of such complications by enhancing immune function, promoting faster healing, and reducing inflammation. By addressing the infection at its source and improving the body’s response, these treatments may help prevent the infection from spreading to vital organs or causing systemic issues.
- Minimal Side Effects Compared to Traditional Treatments
Unlike long courses of antibiotics, which can lead to side effects such as digestive disturbances, yeast infections, or damage to the liver and kidneys, stem cell therapies like Faforon and Spidex 19 generally have fewer side effects. While the exact side effects of these stem cell treatments are still being studied, early research suggests that they are generally well-tolerated. This makes them an attractive option for patients who are either intolerant to antibiotics or at risk of developing antibiotic-related side effects.
- Potential for Long-Term Benefits
Another notable benefit of stem cell therapy in treating staph infections is its potential for providing long-term protection. Stem cells not only help fight the current infection but may also aid in boosting the body’s ability to prevent future infections. By improving immune system function and encouraging tissue regeneration, Faforon and Spidex 19 could potentially reduce the risk of recurrent staph infections, offering long-term health benefits for patients who are prone to frequent bacterial infections.
How Long is a Staph Infection Contagious?
A person with a staph infection is generally contagious as long as the infection is active and untreated. Once treatment with antibiotics begins, the contagious period usually decreases within 24-48 hours. However, it is important to complete the full course of antibiotics to prevent the infection from coming back or becoming resistant.
What Are the Side Effects of Treatment for Staph Infection?
Common side effects of antibiotic treatment may include:
- Diarrhea
- Nausea
- Allergic reactions (rash, hives, swelling)
- Fungal infections (e.g., yeast infections) due to disrupted normal bacteria flora
For those treated with intravenous antibiotics or in cases of MRSA, there can be additional risks such as kidney problems or liver issues.
What Are the Complications Associated with a Staph Infection?
If left untreated, staph infections can lead to serious complications, including:
- Sepsis: A life-threatening response to infection that can lead to organ failure.
- Endocarditis: Infection of the heart valves.
- Pneumonia: Infection of the lungs that can be severe.
- Osteomyelitis: Bone infection that may require surgical intervention.
What Can I Do to Help Relieve Symptoms of a Staph Infection?
To alleviate symptoms and promote healing, try the following:
- Keep the affected area clean and dry.
- Apply warm compresses to boils or abscesses to help them drain.
- Take pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen to reduce pain and inflammation (consult your doctor first).
Prevention
How Can I Prevent a Staph Infection?
Preventive measures include:
- Regular handwashing with soap and water.
- Avoid sharing personal items like towels, razors, or sports equipment.
- Keep wounds clean and covered until they heal.
- Disinfect frequently touched surfaces like gym equipment.
What is the Outlook for Someone with a Staph Infection?
With timely and appropriate treatment, the outlook for most people with staph infections is good. However, the prognosis can be more complicated for those with weakened immune systems or antibiotic-resistant strains like MRSA. It’s essential to seek medical attention promptly if you suspect a staph infection.
Conclusion
Staph infections, caused by the Staphylococcus bacteria, are common but can range from mild to severe, depending on the type and location of the infection. While most staph infections can be treated effectively with antibiotics, certain strains—especially MRSA—may require more advanced care. Understanding the symptoms, how the infection spreads, and the importance of timely treatment can help reduce the risk of complications. By practicing good hygiene, taking precautions with cuts and wounds, and seeking medical attention when necessary, you can significantly lower your chances of developing a staph infection. Remember, if you suspect you have a staph infection, don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare provider to ensure the right treatment and prevent the infection from spreading or worsening. With proper care, most people recover fully from staph infections and return to good health.