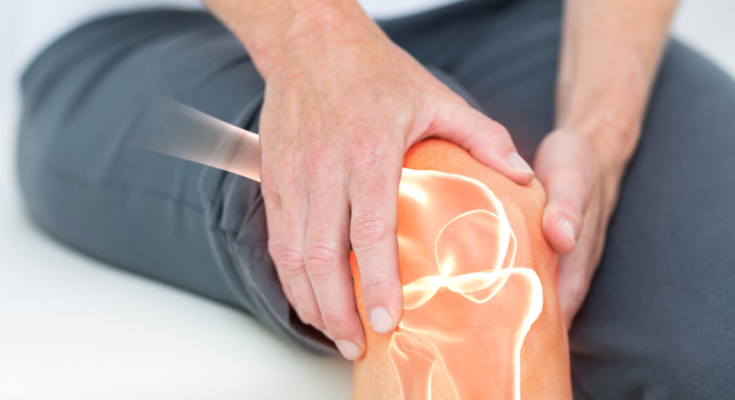
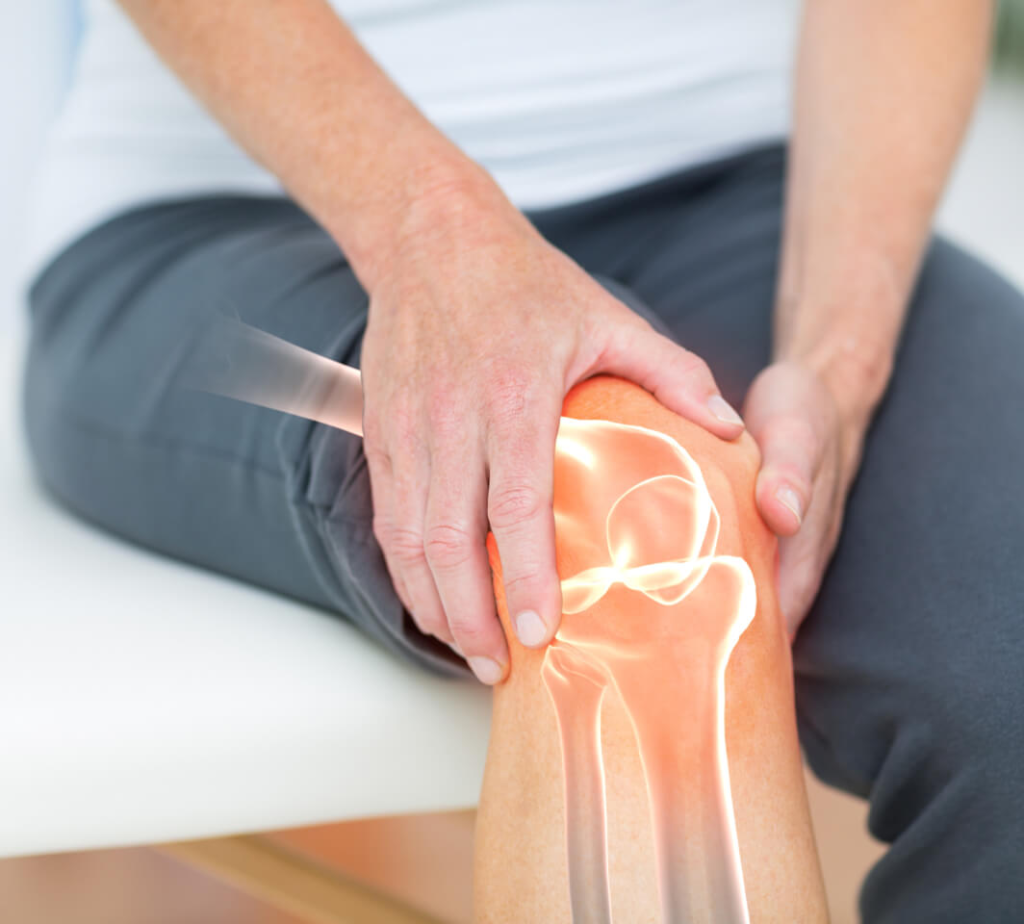
Diabetes is well-known for its impact on blood sugar levels, heart health, and vision, but many are unaware of its effects on bone health. Diabetic bone disease, or diabetic osteopathy, is a lesser-known complication that can lead to increased risk of fractures, bone pain, and decreased mobility.
How Diabetes Affects Bone Health
Both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes can influence bone density and structure in distinct ways, often making bones weaker and more susceptible to fractures. This is due to factors such as:
- Altered Bone Quality: Diabetes affects collagen, a protein essential for bone strength. High blood sugar levels impact collagen cross-linking, leading to weaker, less resilient bones.
- Poor Bone Formation: High glucose levels hinder the ability of osteoblasts (bone-forming cells) to create new bone tissue effectively.
- Oxidative Stress and Inflammation: Both are elevated in diabetes, leading to harmful changes in bone cells.
- Peripheral Neuropathy: Nerve damage from diabetes can affect mobility, increasing the likelihood of falls and subsequent fractures.
Symptoms of Diabetic Bone Disease
Early signs of diabetic bone disease may be subtle or masked by other diabetic symptoms. Some common symptoms include:
- Bone Pain and Tenderness: Persistent bone pain or tenderness may indicate weakened bones or micro-fractures, especially in the hips, spine, or feet.
- Increased Fracture Risk: Diabetics are more prone to fractures even after mild trauma, particularly in areas like the hips and wrists.
- Reduced Mobility: Joint stiffness and limited mobility due to nerve damage or joint inflammation often accompany bone issues in diabetics.
- Swelling in Joints: Inflammatory responses can lead to swollen, painful joints, particularly in the feet and ankles.
- Slower Healing: Bone healing after fractures can be delayed in diabetics, which increases the chance of complications.
Causes of Diabetic Bone Disease
Several factors combine to cause diabetic bone disease:
- Hyperglycemia (High Blood Sugar): Chronic high blood sugar leads to the glycation of proteins in bone tissue, weakening bone structure.
- Insulin Deficiency or Resistance: Insulin plays a role in bone growth, and either deficiency (in Type 1) or resistance (in Type 2) can interfere with this process.
- Inflammatory Response: Diabetes triggers an inflammatory response throughout the body, which affects bone health by promoting bone resorption (breakdown) over formation.
- Vitamin D Deficiency: Diabetics often have lower vitamin D levels, which are crucial for bone health. This can exacerbate bone weakness.
- Reduced Calcium Absorption: Some diabetic medications, like metformin, may interfere with calcium absorption, affecting bone density.
Prevention and Management
While diabetic bone disease is challenging to reverse, several preventive measures can help manage it and reduce the risk of complications:
- Blood Sugar Control: Maintaining blood sugar within target ranges is vital to prevent the progression of diabetic bone disease. Work closely with a healthcare provider to monitor glucose levels and adjust medications as needed.
- Regular Bone Density Tests: Screenings for bone density, such as DXA scans, can help detect early bone loss.
- Nutrient-Rich Diet: A balanced diet with adequate calcium, vitamin D, and magnesium is essential. Foods rich in these nutrients, like leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and dairy, support bone health.
- Weight-Bearing Exercise: Regular physical activity like walking, jogging, or weight lifting strengthens bones and improves joint function.
- Medication Review: Some diabetic medications may influence bone health. A healthcare provider can adjust medications if they’re contributing to bone density loss.
- Fall Prevention: For diabetics at high risk of fractures, measures to prevent falls are essential.
Conclusion
Diabetic bone disease is a hidden but significant risk for people with diabetes, impacting both quality of life and physical mobility. By understanding the causes and symptoms, those with diabetes can take proactive steps to preserve bone health and reduce the risk of fractures.